Management on Rigid-Flex PCB Fabrication
Rigid-flex circuit boards maximize space utilization within electronic devices. The combination of rigid and flexible sections offers three-dimensional routing allowing designers to route traces in unconventional ways, making room for more components and features. This spatial efficiency is valuable in compact and miniaturized products where every millimeter counts. Rigid-flex PCBs also reduce the number of connections and solder joints, lowering assembly costs. This reduced risk of loose or broken connections and wire fatigue improves reliability.
While rigid-flex PCBs offer many benefits, their unique construction presents several challenges during manufacturing. For example, the flexibility of flex sections can cause mechanical stress that can lead to conductor cracking and insulation failures. This requires careful mechanical design to ensure that flex regions can bend and flex without causing damage.
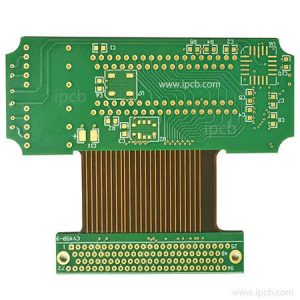
Additionally, rigid flex pcb fabrication must withstand a variety of environmental factors, including moisture and corrosion. These conditions can affect circuit board materials and require specialized testing to validate the integrity of the flexible sections. To ensure the integrity of rigid-flex boards, careful design for manufacturability and close cooperation with fabricators are essential.
Impact of Thermal Management on Rigid-Flex PCB Fabrication
To minimize thermal stresses, a rigid-flex circuit must be able to dissipate heat effectively. This can be accomplished by utilizing components like heat sinks and thermal pads. Additionally, proper spacing between components helps prevent localized heating and the use of conformal coatings can eliminate air pockets that limit heat transfer. Finally, computer-aided simulation and testing can help identify hot spots and areas of high heat concentration so that they can be eliminated or mitigated.
The encapsulated structure of rigid-flex PCBs can also limit the number of components that need to be soldered, reducing assembly costs and simplifying quality control. In addition, it can reduce the number of potential points of failure by eliminating the need for interconnecting cables and wires. Rigid-flex PCBs are a more reliable solution than traditional rigid circuit boards because they are less susceptible to damage from vibrations, shocks and bending, making them a great choice for applications that are subject to a wide range of environmental conditions.
As with any new technology, rigid-flex PCBs can be expensive to produce. This is due to the complex nature of the fabrication process, specialized materials, and the need for rigorous testing and inspections. However, there are a few key ways to reduce the cost of rigid-flex PCBs:
Using industry-standard rigid and flex materials, such as FR-4 and polyimide, can significantly lower the cost of rigid-flex PCB production. In addition, minimizing the layer count and using standardized component packages can further reduce the cost of rigid-flex PCBs.
Another way to reduce the cost of rigid-flex PCBs is to consider a panel-based design. This can save material costs by maximizing the utilization of the material and reducing waste. Furthermore, it can also improve production efficiency by minimizing masking steps and assembly time.